
|
| products
> phenol&derivatives > bpa |
|
 |
|
 BPA BPA |
 |
|
|
 GENERAL GENERAL |
 |
 |
 |
| |
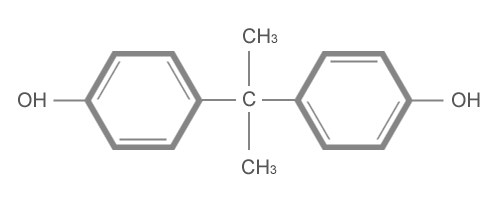
Bisphenol-A(BPA)
is a white, solid chemical produced by recombining
phenol and acetone catalyzed by hydrochloric
acid. BPA also referred to as 2,2-bis (p-hydroxyphenyl)
propane and Diphenyolpropane, has a structure
which makes it suitable as a monomer to produce
polycarbonate, epoxy, phenolic, polyester
and other resins. Used directly as am additive,
it improves the stability of many other resin
systems. The presence of two hydroxyl groups
at opposite ends of the BPA molecule permits
unhindered reaction with a variety of other
chemicals under reasonably mild process conditions
Health and safety information is available
through the appropriate Material Safety Data
Sheet(MSDS). |
|
|
 SPECIFICATION SPECIFICATION
|
 |
| Characteristics
|
Sales Specifications |
| Appearance |
White prills |
| Purity,
wt.%. |
99.85 min |
| Phenol,
mg/kg |
100 max |
| o,p-BPA,
mg/kg |
1,000 max |
| BPX,
mg/kg |
400 max |
|
Water, wt. % |
0.1 max |
|
Iron, mg/kg |
0.5 max |
| Ash,
mg/kg |
100
max |
|
Freezing point, ℃ |
156.5 min |
|
Color, Pt/Co |
5 max |
|
Molten color, Pt/Co |
20 max |
|
 |
|
|
 TYPICAL
PROPERTIES TYPICAL
PROPERTIES |
 |
|
Molecular weight
Appearance
Boiling point, ℃
Melting point, ℃
Flash point, COC
Flash point, CC
Minimum ignition temperature
Lower explosion limit, g/l
Minimum ignition energy, milijules
severity of explosion constant, bar-m/sec
Specific gravity, 25/25℃
Bulk density, kg/dm3
Volumetric resistivity, ohms/cm
Heat of fusin, cal/g**
|
228.29
White prills
360.5
154-157
207
227
532
0.019
1.8
297
1.195
0.59-0.64
5.1 * 1015
32.3
|
|
Specific heat, cal/g/4℃
at 25℃
at 75℃
at 125℃
at 175℃
|
0.35
0.39
0.52
0.51
|
|
"Solubility, g/100g solvent at 25
℃
Acetone
Epichlorohydrin
Ethane
Methnol
Water
|
85
38
150
210
< 0.1"
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
