
|
| products
> phenol&derivatives > ams |
|
 |
|
 AMS AMS |
 |
|
 GENERAL GENERAL |
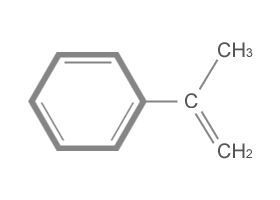 |
Alpha-methylstyrene,
which is also referred to as isopropenyl benzene,
is an organic chemical used to produce a wide
variety of styrenic polymers. AMS adds heat
resistance to ABS resins which can be found
in automotive parts, electronic appliance
housings and protective coatings. AMS is used
in the production of para-cumylphenol, a specialty
intermediate for thermoplastics and polycarbonate
resins. Health and safety information is available
through the appropriate Material Safety Data
Sheet(MSDS). |
 |
|
 SPECIFICATION SPECIFICATION |
 |
| Characteristics |
Sales Specifications |
| Color,
Pt/Co |
20 max. |
| Water,
wt.ppm |
400 max. |
| Purity
*, wt.% |
99.0 min. |
| Inhibitor
content, wt.ppm |
5 - 10
10 - 20 |
| Phenol,
wt.ppm |
15 max. |
| Polymer
content, wt.ppm |
10 max. |
* Purity = 100 - (Total
GC impurities + Water)
|
 |
|
|
 TYPICAL
PROPERTIES TYPICAL
PROPERTIES |
 |
|
Empirical formula
Molecular weight
Appearance
Odor
Autoignition temperature
Boiling point, at 760mm
Critical pressure, atmospheres
Critical temperature
|
C6H5C(CH3)CH2
118.2
Colorless liquid
Pungent, aromatic
573.9 ℃(1065℉)
165.1 ℃(329.2℉)
33.1
383.85℃(723 ℉)
|
|
Explosive limits, by volume in air
Flash point
Closed cup
Freezing point
Heat of vaporization
at boiling point (1 atmosphere)
BTU/lb
Specific heat, ( cal/g/℃)
Vapor
Liquid
|
Lower limit 1.9%
Upper limit 6.1%
53.9 ℃(129℉)
-9.8℃(14.4 ℉)
141.2
0.29
0.49
|
|
Surface tension @ 20℃(dyne/㎝)
Physical state
Reactivity
Refractive index, @20℃
Solubility in water
Specific gravity, @ 20℃
Vapor density, (Air=1)
Liquid at 45℃(113 ℉)
60℃(140 ℉)
80℃(176 ℉)
|
32.40
Liquid
Yes
1.53865
Negligible
0.91
4.1
0.0780
0.0762
0.0738
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
